Note: This notes were strongly inspired by the following books: CSSLP Certification All in one and Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CSSLP CBK, Second Edition
Policy Decomposition
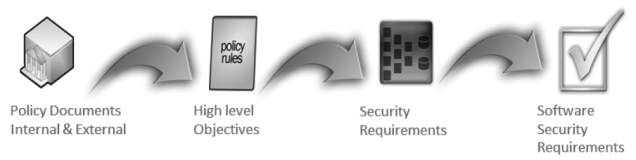
 The policy decomposition is the process of breaking down high level policy requirements into security objectives and eventually protection needs and secure software requirements.
The policy decomposition is the process of breaking down high level policy requirements into security objectives and eventually protection needs and secure software requirements.
Policies involving protecting data could be decomposed in confidentiality requirements.
Policies involving protecting data from unauthorized alteration can be decomposed in integrity requirement.
Policies associated with determining access can be decomposed into availability requirements.
Data Classification and Categorization
Data classification is a risk management tool, with the objective to reduce the costs associated with protecting data.
Types of data :
- structured – the most common form of structured data is that stored in the DB; other forms of structured data, XML, JSON test files, log files.
- unstructured – the rest of data that is not structured; data that is not easily parsed and parsed.
Data states :
- data at rest.
- data in transit – data being transmitted from one location to another.
- date being created.
- data being changed or deleted.
Data labeling
Data classification/labelling is the conscious effort to assign labels (a level of sensitivity) to information (data) assets, based on potential impact to confidentiality, integrity and availability (CIA).
Data ownership:
- Data Owner – (also called information owner or business owner) is a management employee responsible for ensuring that specific data is protected. Data owners determine data sensitivity labels and the frequency of data backup. The Data Owner is responsible for ensuring that data is protected. A user who “owns” data has read/write access to objects.
- Data Custodian – provides hands-on protection of assets such as data. They perform data backups and restoration, patch systems, configure antivirus software, etc. The Custodians follow detailed orders; they do not make critical decisions on how data is protected.
Requirements
Role and user definitions
- objects – items that a user (subject) interacts with in the operation of a system.
- subjects – an active entity on a data system. Most examples of subjects involve people accessing data files. However, running computer programs are subjects as well. A Dynamic Link Library file or a Perl script that updates database files with new information is also a subject.
- actions – permitted events that a subject can perform on an associated object.
Functional requirements
Functional requirements describe how the software is expected to function. They begin as business requirements and are translated into functional requirements.
Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
The RTM is a grid that assists the development team in tracking and managing requirements and implementation details.
You must be logged in to post a comment.